Overview of the development of the copper industry

The development of electrolytic copper foil can be divided into three stages of development: the creation of U.S. copper foil enterprises, so that the world's electrolytic copper foil industry started (1955 - the mid-1970s): Japan's copper enterprises, high-speed development of the world's monopoly on the market stage (1974 - the early 1990s): Japan, the United States, Asia, other copper foil enterprises, such as the multi-polarization of the stage of competition for the market (since the mid-1990s up to the present day)
Currently mainl China is the world's largest producer of copper foil, followed by China, Taiwan Japan. High-end copper foil is still dependent on imports.
In 1955, the U.S. Yates Company began specializing in the production of copper foil for PCBs.
Electrolytic copper foil production process
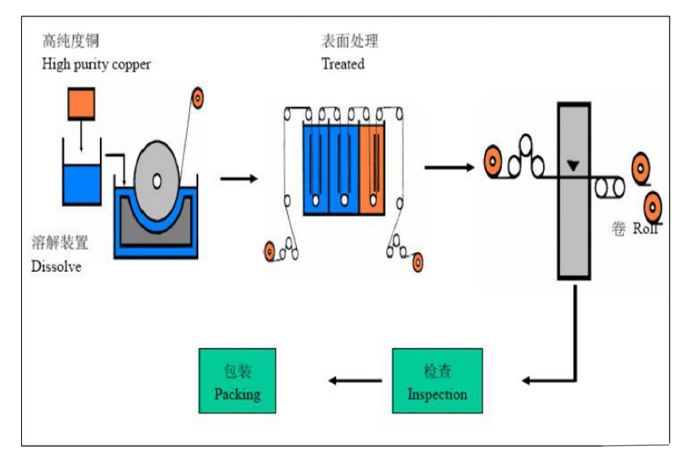
01 Copper Dissolving Flow Chart
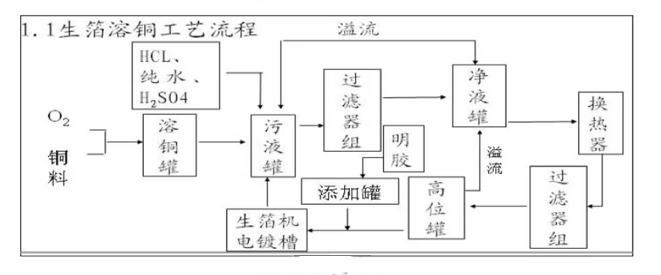
Principle of copper dissolution: Liquefaction (Generation of copper sulfate liquid)
Through the chemical reaction between sulfuric acid copper material in the liquid-making tank under heating condition multi-channel filtration, copper sulfate liquid is generated, then pumped into the electrolyte storage tank with special pump.
Chemical equation:
2Cu+O₂→CuO
CuO +H₂SO4→CuSO4+H₂O
02 Copper Dissolving Tanks Liquid Storage Tanks
In the copper dissolving tank, the content of Cu2+ H+ in the electrolyte is mainly controlled by controlling the amount of reactants the reaction temperature in the copper dissolving tank, the main means are adding electrolytic copper plates on time, recycling electrolyte, adding concentrated sulfuric acid, heat exchanger for heat exchange, adding air by natural convection, etc., to finally generate the electrolyte required for copper foil production.
The liquid storage tank is used to temporarily store the electrolyte flowing down from the copper dissolution tank a small amount of part of the electrolyte flowing back from the foil machine, at the same time provide H2SO4 for the copper dissolution reaction. after circulating between the liquid storage tank the copper dissolution tank, the concentration of H+ in the electrolyte will be reduced, whereas the electrolyte flowing back from the foil contains a higher concentration of H+, thus maintaining the concentration of H+ required for the reaction, ensuring that the reaction proceeds in the direction of the process set. The outlet of the storage tank is connected to the dirt tank, the electrolyte flows into the dirt tank through an overflow pipe.
03 sump
The dirty liquid tank is used to store the electrolyte overflowed from the liquid storage tank part of the electrolyte ed from the foil machine column the electrolyte overflowed from the clean liquid tank. The temperature in the tainter tank is regulated by a plate heat exchanger is controlled at 50°C-60°C. The tainter tank is basically the most important part of the copper melting process. The foul liquor tank is basically the largest part of the entire copper dissolution process, which can play a buffer role in the entire electrolyte cycle, plays an important role in maintaining the continuous stability of the process.
CI-is an important additive in the electrolytic solution, which can directly affect the properties of the foil, avoiding the pinhole phenomenon on the surface of electrolytic copper foil in the electroplating process, improving the leveling of the plating layer reducing the internal stress of the plating layer.
04 Large filter
Large filter filtration is the application of the principle of physical adsorption, the use of activated carbon diatomaceous earth with large porosity, large specific surface area strong adsorption capacity to purify the electrolyte.
The medium of activated carbon filter is activated carbon, which is made of charcoal, high-quality coal or various kinds of fruit s by high-temperature roasting activation. Activated carbon has a lot of capillary pores connected, so the specific surface area is large, according to the test, 1 gram of activated carbon has a surface area of 500 ~ 1000m2. These micropores have strong adsorption effect can adsorb remove pigment, organic matter, residual chlorine, colloids microorganisms in water, thus improving water transparency reducing turbidity.
Diatomaceous earth is an ancient single-cell diatom remains sediments, lightweight, porous, high strength, wear-resistant adsorption filling a series of excellent performance, but also has good chemical stability. It is commonly used in filtration, adsorption, filling, carrier so on.
05 Clear high level tanks
The electrolyte in the clean tank is a cleaner electrolyte filtered through a large filter. In order to maintain the continuous stability of the process, the level of the clean tank is controlled within a certain range, for which the clean tank is equipped with a buoyant liquid level indicator to facilitate the checking of the liquid level. When the level is too high, the electrolyte in the clean tank will overflow back to the dirty tank, which requires the level of the clean tank to be higher than that of the dirty tank.
The main function of the high level tank is to make the electrolyte entering the foil machine have a stable flow rate (or flow). The size of the flow rate is mainly determined by the potential energy difference between the high level tank the electrolytic tank, can also be adjusted by a rotor flow meter. The electrolyte pumped into the high tank from the net tank in the high tank always maintain a certain height, excess electrolyte back to the net tank, the high tank after the electrolyte then add a certain amount of gelatin flow to the cotton core filter.
06 Gelatin tanks wick filters
Gelatin water-soluble protein mixture, it is produced by the skin, ligament, tendon in the collagen by acid or alkali partial hydrolysis or boiled in water, colorless or slightly yellowish transparent brittle flakes or coarse powder, dissolved in 35 ~ 40 ° C water to form a gel (water content of 5 ~ 10 times the weight of the self). The purpose of adding gelatin in electrolyte is to improve the roughness of electrolytic copper foil surface as leveling agent . The mechanism of gelatin is an inhibitory effect: on the microscopic rough surface, the effective thickness of the diffusion layer in the valley is larger than that in the peak, the diffusion speed of the leveling agent (molecules or ions) into the valley is smaller than that into the peak, so that the concentration of the leveling agent in the peak is larger than that in the valley, resulting in the inhibitory effect on the Cu2+ discharge in the peak is larger than that in the valley, so as to achieve the leveling effect.
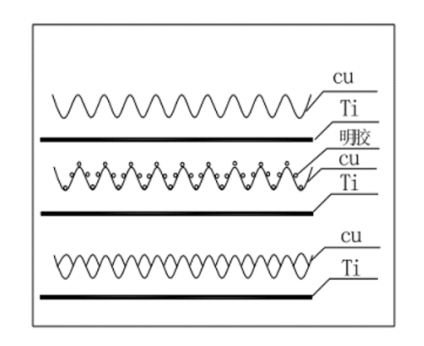
The cotton wick filter is equivalent to a secondary filtration system for electrolyte purification. Its filtering power comes from the level difference between the high level tank the electrolyzer. Generally speaking, one foil machine corresponds to two cotton core filters, so as to facilitate the replacement of cotton core. Cotton core filter mainly filters some mechanical impurities.
07 Raw Foil Manufacturing
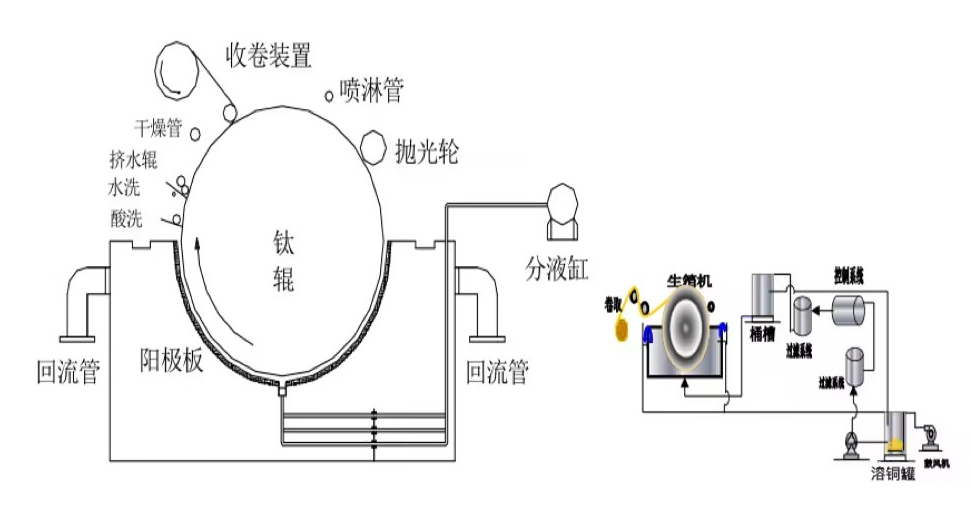
08 Principle of Gross Foil Electrolysis
Gross foil manufacturing uses copper sulfate aqueous solution as electrolyte, the main components of which are Cu+, H+ a small amount of other metal ions OH-, SO42- other anions. Under the action of direct current, the cation moves to the cathode, the anion moves to the anode, the anode is generally used insoluble anode (lead-silver alloy or coated titanium plate, etc.) Due to the different precipitation potentials of the various ions, the content of its composition varies greatly. At the cathode, Cu2+ gets 2 electrons reduced to Cu, which is electrochemically crystallized on the cathode roll surface, the electrode reaction is as follows.
Cu2+ + 2e = Cu↓
On the anode H2O is discharged to produce oxygen H+, i.e., H2O -2e = 2H++O2↑.
Therefore, the whole process is still an acid-making process. Because the oxygen runs away, H+, SO42- combined to form sulfuric acid, i.e., 2H+ + SO42 - H2 SO4
The total reaction is.
CuSO4 + H2O = Cu↓+ H2SO4 + 1/2O2↑
The process of electrolytic deposition of copper involves the generation of a new phase - the electrocrystallization step. Its formation is not accomplished in steps, but by a number of successive steps, viz.
① Diffusion of hydrated copper ions to the cathode surface;
② hydration of copper ions, including the loss of part of the hydration film, so that the copper ions the electrode surface close enough to the loss of water in the main body of the copper ions in the valence electron energy level increased, so that it is similar to the cathode on the Fermi energy level of the electrons, to create the conditions for the transfer of electrons.
③ Copper ions are reduced by discharge at the cathode, forming partially water-lost adsorbed atoms. This is an intermediate state ion, for Cu2+, the process consists of two stages, the first step is Cu2+ + e = Cu+, which is very slow; the second step is Cu+ + e = Cu, partially water-loss rapid exchange of electrons with the cathode for copper ions.
④ The reduced adsorbed ions lose all their hydration layer become metal atoms in the liquid metal;
⑤ The copper atoms arrange themselves into certain forms of metal crystals.
09 Factors affecting the quality of wool foil
① Cu2+ content: Cu2+ content is low, will reduce the current density, brightness current efficiency; Cu2+ content is high, by the solubility limitations in the plating bath wall the pole plate on the precipitation of crystals, the plating solution of the plating capacity will also be reduced, this time, the hardness of the copper foil, strength elongation are high. The concentration of copper ions should be controlled at 65g/L~100g/L.
② H2SO4 content: the presence of sulfuric acid to change the conductivity of the plating solution cathodic polarization, reduce the activity of copper ions, improve the crystalline organization of the plating layer, reduce the tank pressure to achieve high-speed copper plating. Too low sulfuric acid content affects the plating ability produce loose plating, elongation decreased, too high will affect the brightness, copper foil brittle increase the corrosion of equipment. Electrolysis process, more than 85% of the current by the solution of sulfuric acid H + transfer, by the acid content of 130g / L ~ 150g / L or so of copper sulfate solution electrolysis of the gross quality is better.
③ Electrolyte temperature: increase the electrolyte temperature can improve the working current density improve the brightness leveling of the coating. Temperature increase of 10 ° C, the limit current density can be increased by 10%. However, the temperature increase will reduce the cathodization effect, make the crystallization coarser, resulting in metal foil conductivity, elasticity, hardness strength of the decline current density of the use of the range is also narrowed, but the elongation will be improved. Therefore, the temperature should not fluctuate in the production, generally controlled at 50C~65C.
④ electrolyte flow rate: improve the current density must increase the flow rate to promote convective mass transfer reduce the concentration of polarization, to obtain uniform deposits. Japan's test proved that in the flow rate of 2m / s, when the current density increased to 25000A / m2, you can still get a smooth dense electrolytic deposit layer. However, at this time, the cathode anode distance is only 5mm, the equipment requirements are very strict.
⑤ Current Density:Increasing current density is one of the important measures to improve production. At present, the current strength of raw foil production in 20000A ~ 50000A, current density in 3500A / m2 ~ 13000A / m2. current density will increase the electrochemical polarization concentration polarization, the number of generated nuclei increased, the results of the foil finer, but the current density is too high will produce a tumorous or dendritic plating layer.
⑥ Additives: add an appropriate amount of additives to the electrolyte, can increase the cathodic polarization to varying degrees inhibit the abnormal growth of metal, which is conducive to obtaining dense cathodic deposits, improve the elasticity, strength, hardness smoothness of copper foil. The amount of additives must be appropriate, if too much is added, not only the tank voltage rises, but also the gross surface of the hair foil appears streaks, the copper foil becomes brittle. Due to the adsorption of additives, some metal impurities, such as arsenic, antimony amphoteric oxides, may also be composed of complexes with surface-active substances adsorbed on the cathode, so the additives would rather add less than more. The amount of additives added is also closely related to the temperature, high temperature, the amount of additives added is large, so the temperature should be controlled to prevent too large fluctuations.
(7) cathode roller speed: in the case of current determination, roller speed is the most important factor in determining the thickness of copper foil. The following formula is commonly used to calculate.
W=l×K×η/60×L×M)
Where: W a Chin roller speed; m/min
I a current; A
K an electrochemical equivalent; g / (A.h), copper K is 1.186
η - current utilization rate; %
M a stardized weight; g/m2
L - cathode roll width; m
10 Gross Foil Mechanism Manufacturing
① Anode plate: At present, the materials of anode plate adopted by the company are lead-silver alloy titanium anode (DSA). Among them, the anode plate made of lead-silver alloy material is repeatedly dissolved deposited during the reaction process, forming passivation layer on the surface to achieve the "insoluble" state. However, as the electrodes continue to corrode, the cathode anode spacing gradually becomes bigger, the tank pressure becomes bigger, which greatly increases the consumption of electric power, the flow rate of the inner tank is affected by the uneven corrosion, making the plating layer uneven. Impact, making the plating layer uneven.
The DSA that uses iron surface coated with yttrium oxide other materials as insoluble anode s precious metal oxides such as nails palladium with catalytic activity to be coated on the substrate to become insoluble anode. Due to the electrocatalytic effect of the surface precious metal oxides, the effect of the electrode interface electric field on the reaction rate is enormous. With the increase of the electrode reaction overpotential, the reaction rate can be increased by 10 orders of magnitude. At the same reaction rate (i.e. current density), DSA can get very low overpotential, thus having high energy conversion efficiency.
② Auxiliary cathode: In order to prevent copper from being electrodeposited on the side of the cathode roll during electrolysis, which affects the production of copper foil, an auxiliary cathode is provided on each side of the electrolyzer, which is made of copper rod. In the process of copper electrodeposition, the current between the cathode anode is not uniformly distributed, especially at the edge of the cathode anode rolls, the distribution of power lines is more dense, so that the plating layer produces the "edge effect". For this reason, the role of auxiliary cathode is to absorb the edge of the titanium cathode rolls on both sides of the power line, reduce the edge effect to reduce or eliminate the burr edge tearing other undesirable phenomena. In the actual production of auxiliary cathode can not completely eliminate the edge effect, need to seal the edge of the titanium roller rubber O-ring with.
③ Polishing device: after copper foil production for a period of time, the cathode roll surface will produce some oxidized layer some minor unevenness, so it is necessary to deal with this situation, usually using nylon brush roll to carry out. Generally speaking, the cathode roll surface is polished once after every roll of copper foil is produced. When the unevenness of the roll surface the oxidized layer other problems are more serious, it is necessary to take out the cathode roll send it to the grinding roller room for surface treatment.
④ Squeeze water: the role of the water squeeze roller is mainly to squeeze off the hair on the "water", the flatness softness of the roller surface on the gross surface of the wool foil has a certain impact on the nature of the gross surface, when the water squeeze roller is not flat, it will cause scratching of copper foil other situations, while the "water" for the squeezing of clean will increase the temperature required for baking. At the same time, "water" to squeeze clean will increase the temperature required for baking, increase the consumption of electricity. Nowadays, the commonly used squeezing roller in the workshop is rubber type. When the squeezing roller becomes soft absorbent, it not only reduces the temperature required for drying the water on the surface of the copper foil, but also protects the hairy surface of the copper foil from being "harmed".
11 Roughing process
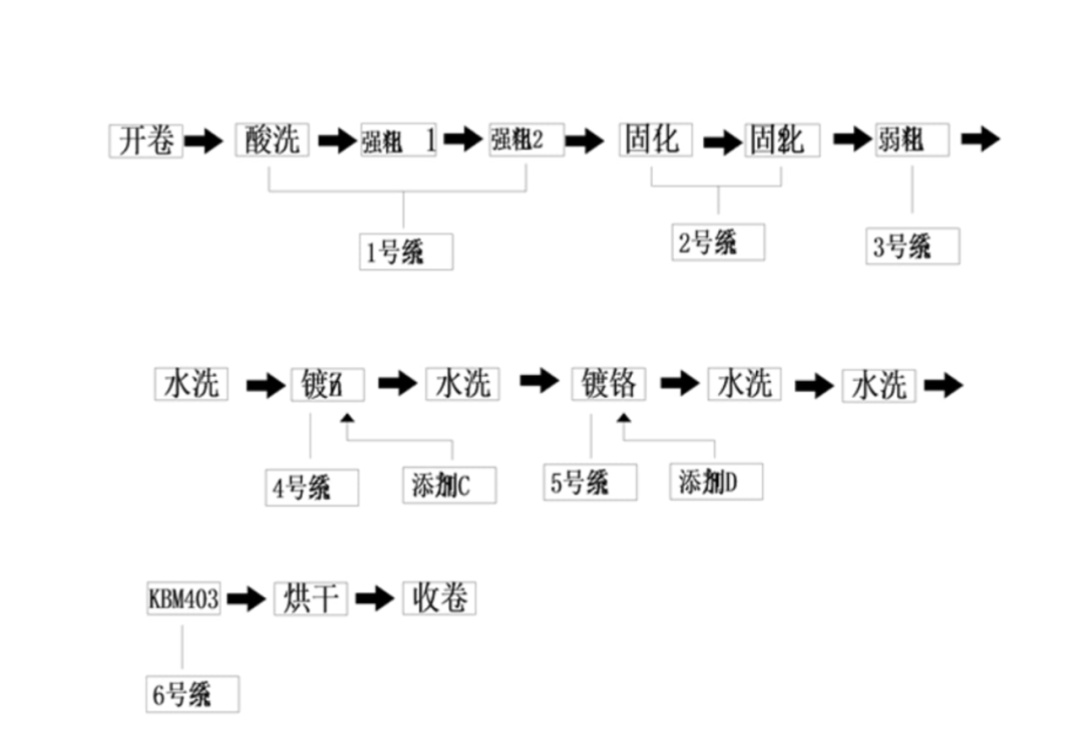
Acid washing is the process of cleaning the surface of the wool foil to remove the oxidized layer etching the surface of the foil. The wool foil has a short storage process after the production of the foil machine, the oxidized layer is easy to be generated on the surface in the air, which must be removed before the roughening process. The electrolyte with high acid content is used for pickling, it the electrolyte needed for roughening are both from the 1# tank. The surface of the foil will be cleaned cooled down by nozzles before after entering the roughening tank to remove the impurities on the surface of the foil cool down the surface of the copper foil to minimize the effect on the roughening of the foil.
The roughness of the rough surface of the copper foil coming out of the foil machine fails to meet the requirements of the platen, so it is necessary to carry out a certain degree of roughening on the rough surface of the rough surface to increase the roughness of the rough surface. Strong roughening is carried out for the purpose of making better bonding between the copper foil the substrate. Strong roughing in the roughing section to be carried out twice, on the one h by the equipment transmission speed limitations, a shorter period of time a roughing can not reach the required roughness of the pressure plate, on the other h by the impact of the current, in a shorter period of time to have a better roughness of the foil will have to need a larger current, a larger current is easy to lead to the etching process after the pressure plate of the residual copper, which is mainly due to the current in the case of the large This is also mainly due to the high peak value of the roughening under high current. The electrolyte for strong roughening is copper sulfate solution with high acid content. The principle of strong roughening is
Anodic reaction 2H2O-4e=4H++O2↑
Cathode reaction Cu2++2e=Cu↓
Total reaction 2Cu2++2H2O=2Cu+4H++O2↑
Due to the low concentration of copper ions in the electrolyte, in the case of insufficient Cu2+ ions, it also causes the oxidation of copper to form "copper powder" uniformly distribute it on the surface of the foil to form a concave-convex surface, which also leads to the uneven distribution of the local electric current on the surface of the foil, the uneven electrodeposition of copper ions which makes the surface of the foil even rougher.
14 solidification (chemistry)
The roughness of the copper foil is changed during the roughening process by the adhesion of "copper powder" to the hair surface.
The adhesion of the "copper powder" to the rough surface is not good, so curing treatment is also necessary. The principle is that the roughness of the copper foil is reinforced by electrodeposition of a thin film of copper on the rough surface of the copper foil. The curing process differs from the roughing process in that the concentration of copper ions in the electrolyte is significantly higher in the curing process than in the roughing process, so that the curing process is mainly characterized by copper deposition.
15 coarsening of weak points
The purpose of weak roughening is to increase the roughness of the rough surface of the copper foil after curing, so that there is a better bonding between the copper foil the substrate to meet the requirements of the platen. The concentration of copper ions in the weakly roughened electrolyte is reduced compared with the strong roughening, but new arsenic pentoxide is added, the current density is also greatly reduced. The large decreases in copper ion concentration current density indicate that the amount of electrodeposited copper "copper powder" in the weak roughened electrolyte is significantly lower than in the strong roughened electrolyte, also indicates that the new "plating" on the surface of the foil is dominated by electrodeposited copper. The precipitation potentials of As5+ Cu2+ are very close to each other, the concentration of As5+ is also very small, so the deposition of As5+ Cu2+ on the surface of the foil can form an alloy plating, which can improve the roughness of the foil. At the same time, the presence of As can also accelerate the electrodeposition of copper ions. The principle of electrodeposition of As is as follows.
As2O5+3H2O=2H3AsO4
H3AsO4 +2H+ + 2e =HAsO2+ 2H2O
HAsO2+3H+ +3e =As↓+ 2H2O
In controlling the concentration of arsenic, it is controlled at 1.70.2g/L to guarantee that the copper foil has better performance appearance.
The purpose of chromium plating is to passivate the zinc coating, because the surface of metallic chromium is prone to generate a stable oxide layer Chromium plating, like zinc plating, has to be plated on the hairy glossy surfaces of the copper foil. The electrode reaction is
Cathode: Cr2O72-+14H+6e→2Cr3++7H2O
Side reaction: 2H2O+2e-H2↑+2OH
Anode: OH--2e-O2↑+H2O
Before chromium zinc plating, there will be a step of water washing process, the purpose of water washing is mainly to wash off the residual ions impurities on the surface of the copper in the previous step in order to eliminate the influence on the zinc plating or chromium plating, at the same time, it can also be used to regulate the surface of the copper foil due to the drive rollers the heating caused by the reduction of the temperature of the chromium plating or zinc plating.
17 Coupling agent treatment
KBM403 is a kind of silane coupling agent containing epoxy group, its chemical name is r-(2,3-epoxypropyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane, the chemical structure formula is CH2-CH(O)CH-O(CH2)3Si(OCH3)3. Appearance is a colorless transparent liquid, soluble in organic solvents, such as acetone, benzene, ethyl ether, halogenated hydrocarbons hydrolyzed in water. Boiling point 290C, density P25′g/m11.065, refractive index ND25: 1.426, flash point 110°C, content ≧ 97%. Domestic commonly used KH-560 as an abbreviation, the United States is used A-187 as an abbreviation. KBM-403 is usually made into dilute aqueous solvents to use, the concentration of its aqueous solution is usually about 0.1-2.0%. It is widely used in glass fiber reinforced epoxy resins, ABS, phenolic resins, nylon, PBT, etc. It can improve the adhesion of inorganic fillers, substrates resins in order to improve their physical properties, especially the mechanical strength, waterproofing, electrical properties, heat resistance other properties of composites, it has a high retention rate in the wet state.
KBM403 is diluted then sprayed on the gross surface of the copper foil by piping under the action of a metering pump then dried. Coating KBM403 on copper foil can improve the bonding of copper foil to the substrate improve the peel strength of copper-clad laminates.
KBM403 is very easy to hydrolyze in water, its hydrolysis reaction is as follows.
R-Si-(OR)3+H2O
R-Si-(OR)2(OH)+ROH
R-Si-(OR)2+H2O
R-Si-(OR)(OH)2+ROH
R-Si(OR)+H2O R-Si(OH)3+ROH
The Si-OH bond in its hydrolysis product -Si-OH is very active can combine with metal bond to form -Si-Metal bond, thus adhering to the metal surface, in addition, the hydrolysis product is also easy to self-condensation to form -Si-Si- leading to the KBM403 can't play the role of adhesive, by adjusting the PH value can be controlled by the self-generated condensation. Pressure plate, by the theory of adsorption can be seen, containing adhesive between the copper foil the substrate by the pressure, adhesive the distance between the molecules of the bonded material reached 10-5A, the interface between the molecules will produce mutual attraction, so that the distance between the molecules to further shorten to be in the maximum stable state, thereby improving the peeling resistance of copper-clad plate.
Gross surface crystal phase structure of electrolytic copper foil
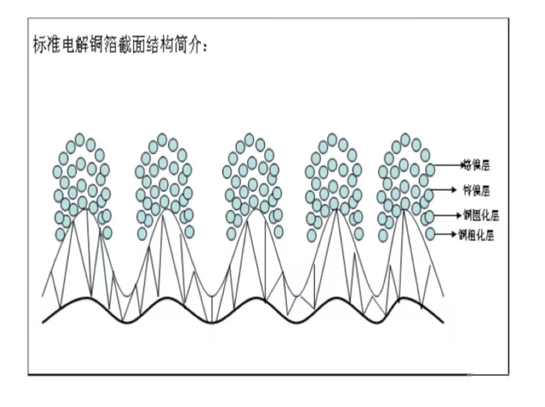
In order to prevent the residual moisture from harming the copper foil, it must finally be dried at a temperature of not less than 100°C. When drying, the temperature must not be too high.
The slitting process slits classifies the finished copper foils according to the customer's dem packages them well.