Chapter 1: Classification Performance Parameters of Energy Storage Battery
The energy storage battery is the core part of the energy storage system, accounting for about 60% of the total cost of the energy storage system. Unlike power batteries, energy storage batteries are widely used in power system segments such as power generation, transmission distribution, power consumption with their functions of peak shaving valley filling, system frequency regulation, smoothing new energy power output.
According to the direction of downstream application, it can be divided into three directions: power generation side (to solve the problem of grid instability caused by the intermittency volatility of wind power generation), grid side (to maintain the stable operation of the grid), user side (to reduce peaks valleys save the user's electricity bill).
The more widely used at this stage are lead storage batteries lithium batteries.
Chapter 2|Battery Main Performance Parameters
Ah (ampere-hours)
Reflects battery capacity, For example, 48V100Ah means the capacity of the battery is 4.8 degrees of electricity. Nominal voltage nominal ampere hours are the most basic core concepts of batteries. Electricity Wh = power W * hours h = voltage V * ampere hours Ah.
C (Battery Discharge C Multiplier)
Reflects the battery charge/discharge capacity multiplier. Charge/discharge ratio = charge/discharge current/rated capacity. A measure that indicates how quickly or slowly a battery is discharged. Generally, the capacity of the battery can be detected by different discharge currents. For example, if a battery with a capacity of 100A-h is discharged at 15A, its discharge multiplier is 0.15C.
DOD (Depth of Discharge)
refers to the depth of discharge of a battery during use. The percentage of capacity discharged by a battery versus the rated capacity of the battery. For the same battery, the depth of DOD set is inversely proportional to the cycle life of the battery. When enhancing one aspect of performance, it sacrifices other aspects of performance. For example, at 80% DOD, the cycle life of Li-ion battery can reach 6,000 ~ 12,000 cycles.
SOC(State of charge)
Indicates the percentage of the remaining battery charge to the rated capacity of the battery.
SOH(State of Health)
Battery health status (including capacity, power, internal resistance, etc.) is the ratio of the capacity discharged by a battery from a fully charged state at a certain multiplication rate to the cut-off voltage to its corresponding nominal capacity.
Simply put, it is the ratio of the performance parameters to the nominal parameters of the battery after a period of use, 100% for new batteries from the factory, 0% for completely obsolete batteries., according to IEEE stards, batteries should be replaced after they have been used for a period of time the capacity of the battery when fully charged is less than 80% of the rated capacity.
tripartite
Generally referring to a device that charges in three stages, three-stage charging is an automatic charging process, with constant current, constant voltage float charging being the three necessary stages of three-stage charging.
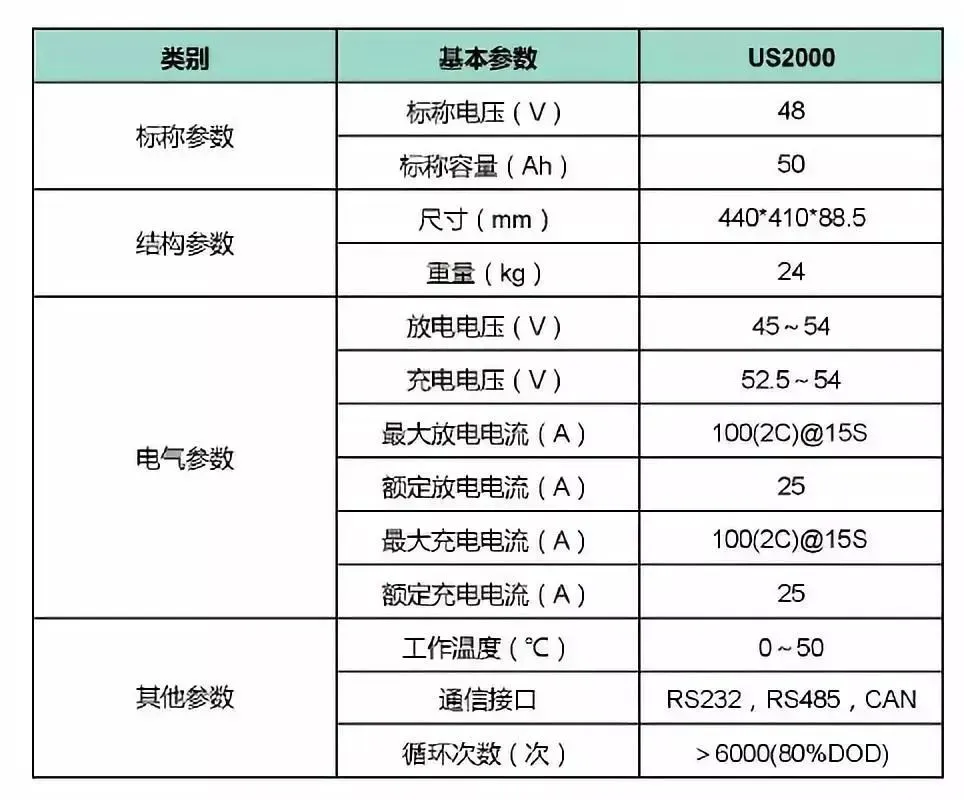
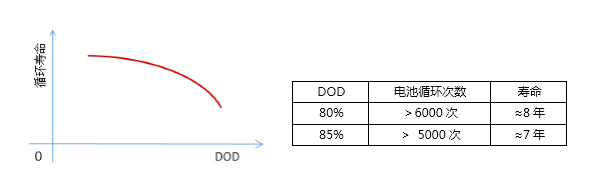
Chapter 3: Trends in Energy Storage Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries gradually replacing lead-acid batteries
Batteries are a more efficient way to store energy. Lithium-ion batteries have the advantages of low environmental pollution, high energy density, long cycle life, strong multiplier performance, As its cost declines the economics of lithium-ion batteries are starting to come into sharper focus, their application in the energy storage market is becoming more widespread.
Lithium-ion batteries are more widely used in new battery storage facilities, the stock of lead-acid batteries already in use is gradually being replaced by lithium-ion batteries. Future,The market for lithium-ion batteries for energy storage has greater prospects for development.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are favored
In the energy storage lithium-ion batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries have more advantages compared to ternary material batteries, is the mainstream direction of the future development of lithium-ion batteries, the main reason is: energy storage batteries are mainly concerned about the economics of battery production use, more consideration is given to the cost of the battery, cycle performance, total life cycle costs other factors. Therefore, lithium iron phosphate batteries are favored for their low production cost, high cycle times other advantages.